

When talking about spina bifida detection, the process of identifying a neural tube defect in a developing baby before birth. Also known as neural tube defect screening, it helps parents and doctors plan early care and make informed choices.
Spina bifida detection sits inside a bigger system of prenatal screening, a series of tests that check a fetus’s health during pregnancy. One of the most common tools in this system is ultrasound, an imaging method that creates real‑time pictures of the baby’s spine and brain. Ultrasound requires a skilled technician and a clear view of the fetal anatomy, and it enables doctors to spot spinal malformations as early as the first trimester. Another key player is the alpha‑fetoprotein (AFP) test, a blood test that measures a protein linked to open neural tubes. High AFP levels often indicate a higher chance of spina bifida, prompting follow‑up imaging.
These three entities—prenatal screening, ultrasound, and AFP testing—form a chain: prenatal screening includes AFP testing, AFP testing signals the need for detailed ultrasound, and ultrasound confirms the diagnosis. Together they create a reliable pathway for early detection, giving families time to explore options like fetal surgery, specialized neonatal care, or early intervention programs.
Finding spina bifida early isn’t just about knowing the diagnosis; it shapes the whole care plan. Once a defect is confirmed, doctors often discuss medication strategies such as high‑dose folic acid supplementation, which research shows can reduce the severity of neural tube defects. Our site also offers deep dives into medication safety, like comparisons of steroids (deflazacort vs. prednisone) and antihistamines, so readers can understand how any drug they take during pregnancy may interact with fetal development. Knowing the exact type of spina bifida—myelomeningocele, meningocele, or occulta—helps specialists decide whether fetal surgery is an option or if post‑natal interventions like shunt placement are needed.
Beyond medicines, early detection influences lifestyle advice. Parents learn about proper nutrition, the importance of avoiding teratogens, and the role of prenatal vitamins. Our collection includes articles on supplement safety and disease prevention that can guide expectant mothers in making healthier choices. For example, an article on “How Climate Change Affects Immunodeficiency Patients” highlights how environmental stressors might impact a pregnant person’s immune system, which is valuable information for families managing a spina bifida pregnancy.
When a diagnosis is confirmed, families often seek support resources. Counseling, social services, and specialist networks become part of the care plan. Early screening results give these teams a head start to coordinate appointments, arrange for pediatric neurosurgeons, and set up early intervention therapy. All of this reduces emergency visits after birth and improves long‑term outcomes for the child.
Our curated articles below expand on each piece of this puzzle. You’ll find side‑by‑side drug comparisons that clarify which steroids are safest during pregnancy, detailed looks at how certain illnesses (like Legionnaire’s disease) could complicate a pregnancy, and practical guides on buying generic medications online—useful if you need to manage costs after a spina bifida diagnosis. Each post is written to give clear, actionable advice without medical jargon.
So whether you’re just starting prenatal visits, have just received an elevated AFP result, or are preparing for a detailed ultrasound, the information ahead will help you understand the steps, the choices, and the resources that can make the journey smoother. Dive into the articles below to get the facts you need, compare treatment options, and see how expert guidance can support you and your baby through every stage of spina bifida detection and care.
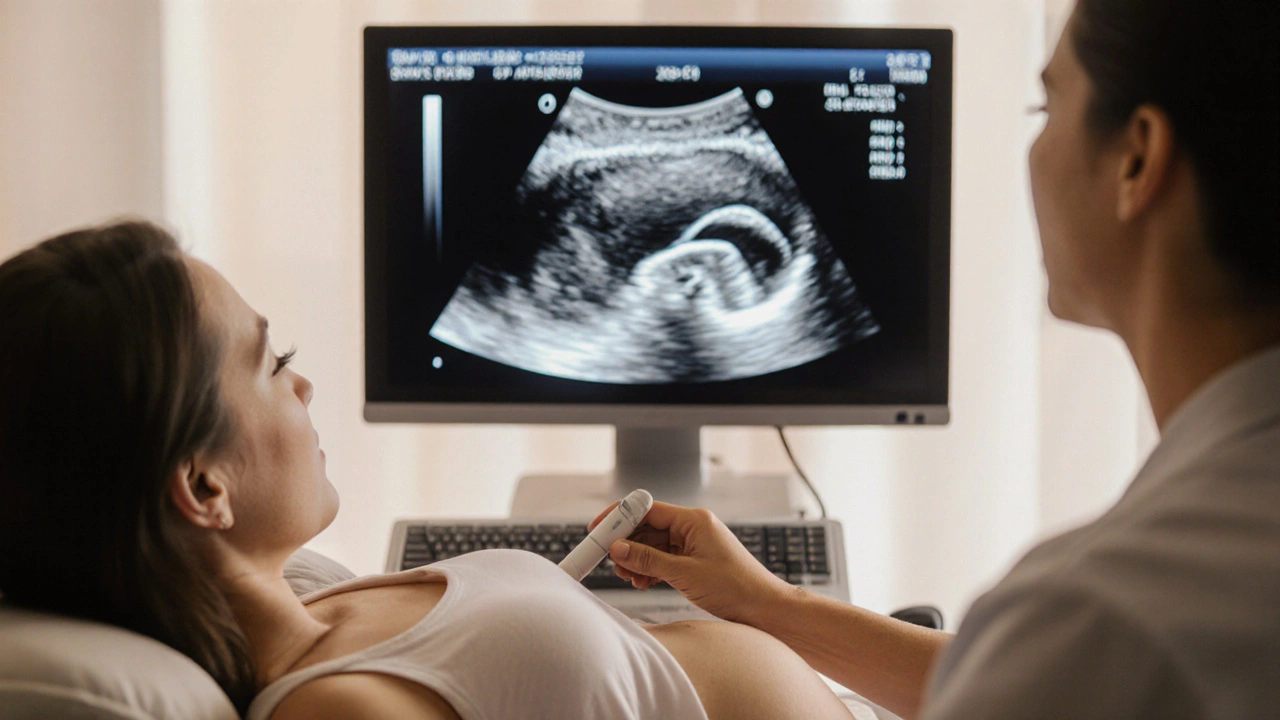
Learn how ultrasound detects spina bifida in unborn babies, optimal scan timing, accuracy, complementary tests, and what steps to take after a positive screen.